“Video conferencing works by capturing audio and video from participants, compressing the data, transmitting it over the internet using real-time protocols, and decoding it on the receiver’s device to enable live communication.“
Remote work, online classes, video podcasts, global conferences, virtual concerts and live shopping sessions are evidence that video conferencing has become a part of our lifestyle.
This article is an in-depth guide on the technology, demonstrating its workflow, features, use cases and challenges. Businesses looking forward to building their own apps can make use of this post to understand the feature thoroughly.
What Is Video Conferencing?
Video Conferencing is a real-time technology that uses audio and video to simulate face-to-face communication between individuals or groups located in different places.
This technology is adapted in business platforms to drive remote collaboration. Especially in corporate communication, Video conferencing reduces travel costs and enables instant communication among internal and external stakeholders.
Market size
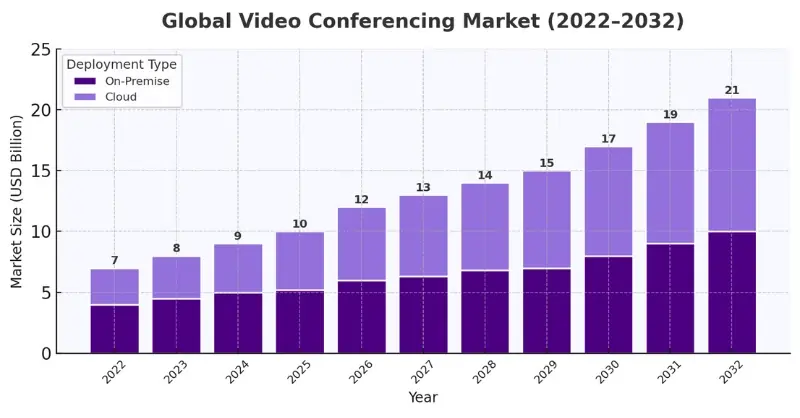
Source: https://market.us/report/video-conferencing-systems-market
As per the article Status, Challenges and Trends in Videoconferencing Platforms published in 1. Vol. 18 No. 3 (2023): International Journal of Computers Communications & Control (June):
The global video conferencing market is projected to grow from USD 7.65 billion in 2022 to USD 18.56 billion in 2030.
This represents a 142.6% increase over the 8-year period.
Evolution
Back in the 1920’s Video Conferencing was only a mechanical-analog technology, limited exclusively for corporate use.
With years, Video Conferencing became more accessible and affordable, and sooner transitioned into a commodity item. By 2020s. It fully transformed into an IP-based service.
Especially, between March – April 2020 the usage peaked with the pandemic and then the market began losing its momentum in the second half of 2020.
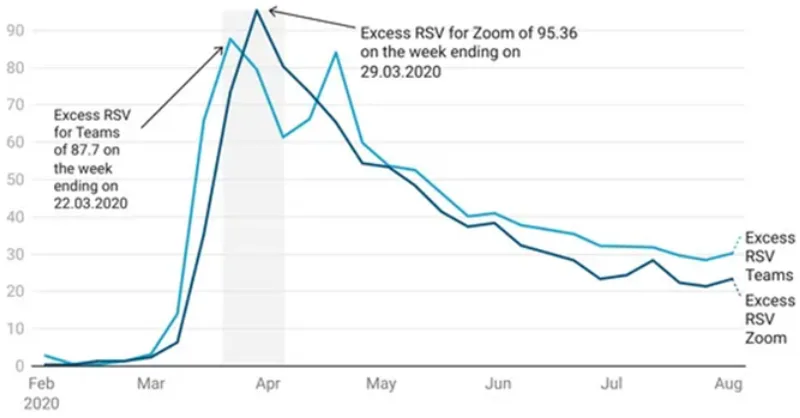
Source: https://www.mdpi.com/2079-9292/11/16/2633
Although the graph showed a decline post-April 2020, pointing to countries lifting COVID-19 restrictions, the demand for Video Conferencing remains high. This period shows us 2 important shifts:
- Activities like work, education, and healthcare started transitioning towards semi-virtual operations.
- The increased use of Video Conferencing impacted the consumer-purchasing decisions
Subsequently, the future is open for plenty of advancements with trends leaning to AI integration, VR and improved bandwidth.
How Does Video Conferencing Work In An App?
When you start a video call, a lot is happening behind the scenes.
In this section, we will explore the underlying architecture, and the working process of video conferencing within an app.
Design and Architecture
Each Video Conferencing app available in the market has unique architectural patterns. How do the teams select a particular pattern depends on the core idea of their business, and where the Video Conferencing will be implemented.
This decides how your app will look, work and deliver the video experience to your users.
However, in this guide, we will cover the most common approaches in terms of design, development and deployment.
Core Architectural Components
In the web, a video conferencing system comes in several main layers:
- User interface
- Conference control
- Control plane
- Media plane
- Administrative interface
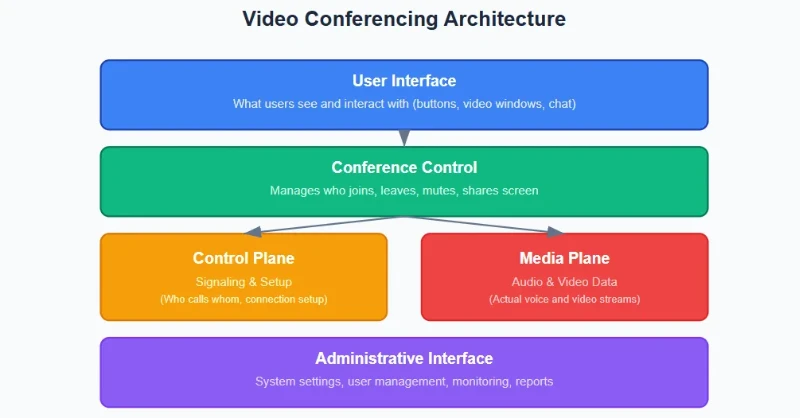
The User Interface is the layer where your customers can access your platform. This is what users can look at as an app.
On the other hand, the Conference Control has the components that are needed for creating a meeting, adding users and removing meetings.
Users can click on the button on the UI layer to manage the conference actions in the conference control layer.
Meanwhile, the Control plane takes care of the incoming and outgoing connections using signaling protocols like Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) or H.323. These protocols connect the endpoints of a conference with mixers in the Media Plane.
The Media Plane takes care of the video and audio streams managing their codec specifications, type of Real-time Transport Protocol (RTP) payload, and other parameters like size.
These are the basic layers in video conferencing. Developers choose different architecture for building a Video Conferencing system based on specific requirements.
Network Topology Architectures
WebRTC is a core technology behind Video Conferencing. Several researches identify 3 main network topologies under the WebRTC architecture:
- Peer-to-Peer (P2P) / Mesh
- Multipoint Control Unit (MCU)
- Selective Forwarding Unit (SFU)
Ⅰ. Peer-to-Peer (P2P) Architecture
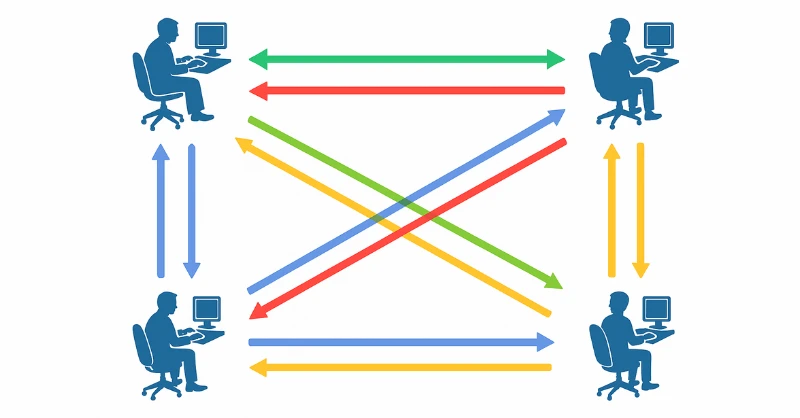
The P2P network topology, also known as the mesh topology, establishes a direct connection between participants to exchange media. They do not use any intermediate server to exchange the audio and video streams.
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| ⬆️Low cost | ⬇️Heavy bandwidth |
| ⬆️HQ service | ⬇️High processing power |
| ⬆️Easy implementation | |
| ⬆️WebRTC deployment |
Ⅱ. Multipoint Control Unit (MCU)
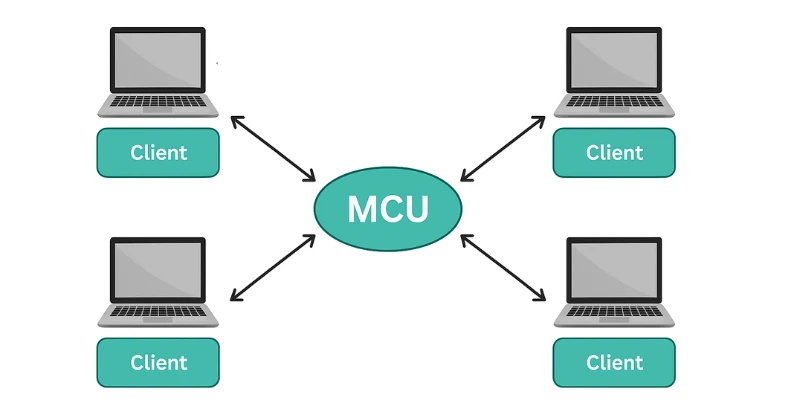
As the name indicates, the MCU connects multiple participants in a video conference through a central MCU server.
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| ⬆️ Efficient CPU usage | ⬇️ Server side complexity |
| ⬆️ Low Bandwidth | ⬇️Heavy resource |
| ⬇️Packet Loss | |
| ⬇️Inflexible layout | |
| ⬇️High cost |
Ⅲ. Selective Forwarding Unit (SFU)
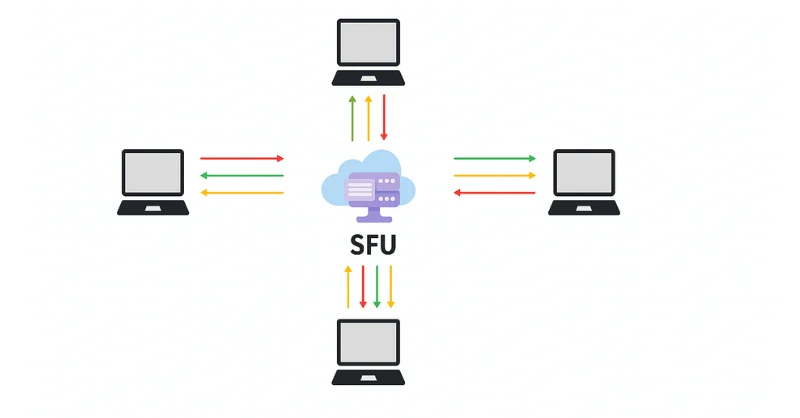
The SFU topology is a modern architecture and by a popular approach among several video conferencing platforms. This P2P and MCU alternative directly receives media streams from each participant and forwards them to other participants without any decoding.
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| ⬆️ Scalable | ⬇️ Server side complexity |
| ⬆️ Less expensive |
Tech Stack
Ⅰ. Core Technologies
1. WebRTC
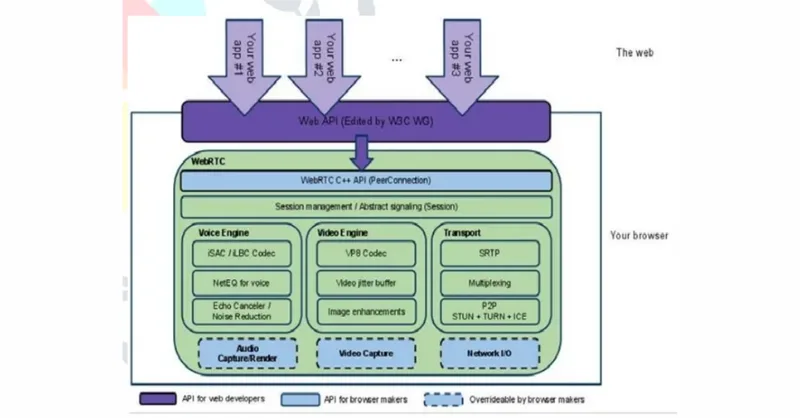
Source: https://www.jetir.org/papers/JETIR2205908.pdf
✅ WebRTC is a combination of 3 layers:
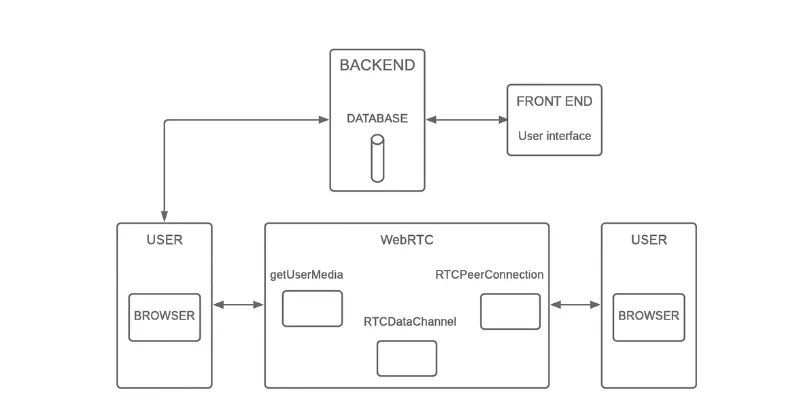
- Web Developer API Layer: This is the JavaScript API that web developers use to build real-time communication apps. It includes:
- RTCPeerConnection
- getUserMedia()
- RTCDataChannel
- Browser API Layer: This handles the core WebRTC functionality within the browser, managing the audio and video codecs, encryption, and network protocols.
- Custom Service Layer: These are browser-specific implementations that handle the low-level networking and media processing.
In general, the challenge in video conferencing with WebRTC is – most devices sit behind NATs (Network Address Translation) or firewalls. This makes direct P2P connections almost impossible.
✅ WebRTC solves this through a coordinated process:
- To initiate connection with Client B, Client A contacts a Signaling Server (not a part of WebRTC, developers must implement this).
- Before a P2P connection happens, the Signaling server exchanges the metadata between the clients, handles the session descriptions (SDP – Session Description Protocol) and coordinates the ICE candidates to establish potential connection paths. Once these tasks are done, the Signaling server steps aside.
- Next, a STUN server (Session Traversal Utilities for NAT) helps Clients A and B to discover their public IP address to check if they are behind NAT. On the other hand TURN (Traversal Using Relays around NAT) stays ready to act as a relay server to forward the traffic between clients.
- Simply put, the clients discover connection paths via the STUN/ TURN server, and start exchanging their connection information through the Signaling server. This establishes a direct P2P connection where real-time audio, video, or data flows directly and smoothly between each other.
- Apart from WebRTC, a Video Conferencing system might also use JavaScript, HTML5, CSS3 or React/Vue/Angular for the frontend.
2. Socket.IO
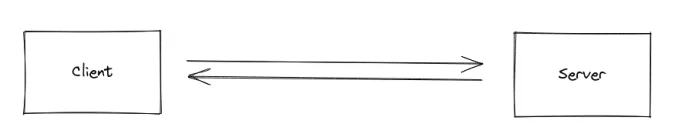
To connect a Client and a Server directly and establish bidirectional communication, Video Conferencing systems generally rely on a WebSocket library like Socket.IO.
In a web video conferencing infrastructure, this JavaScript library uses WebSocket + Engine.IO to implement transport-based two-way communication layers between browsers and devices.
If your platform relies on more than one Socket.IO server, it is best to use in-memory Redis data store and Redis Adapter
3. Redis
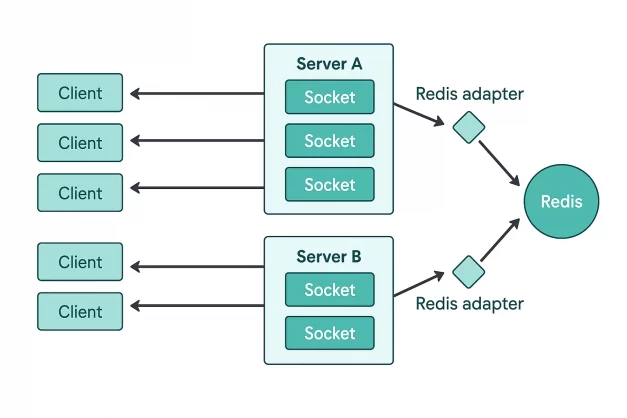
Video conferencing apps involve a lot of data and the systems require a data store that can easily handle multiple operations at the same time and manage to deliver calls with ultra-low response time.
This is where Redis, an open source in-memory data store comes in. It offers an append-only log in the form of a data structure, supporting native data types including lists, strings, hashes, sets and sorted sets.
Besides Redis, video conferencing platforms also rely on database and storage systems like MongoDB/PostgreSQL or AWS S3/Cloud Storage.
4. Node.js
More often, Node.js is the Control Plane layer that serves as a signaling server that coordinates WebRTC P2P connections, as discussed above.
Beyond signaling for initial client handshake, Node.js manages critical functions like room creation and management, user authentication, participant controls, and integration with STUN/TURN servers for NAT traversal.
For multi-party calls, Node.js handles the connection with media servers (SFU/MCU) for routing the streams and handling the audio-video mixing.
It also is responsible for providing REST APIs for scheduling meetings, integrating FFmpeg/ GStreamer to process the video/audio recordings, and taking care of challenges like load balancing and session persistence when there are multiple server instances concurrently.
Note: For media transmission, a Video Conferencing system might also make use of servers like Kurento, Janus or mediasoup apart from SFU/ MCU.
5. Express.js
We’ve mentioned in the above para about Node.js providing REST APIs for meeting management and processing tasks. To carry out this process the signaling server Node.js requires a HTTP server foundation and web framework like Express.js.
This web app framework works alongside Socket.IO to provide both traditional HTTP request handling and real-time signaling capabilities.
This framework provides the endpoints to schedule and manage meetings by handling the initial web page delivery that loads the WebRTC client-side code.
On the other hand, it takes care of security (CORS, authentication tokens), request parsing, and logging by managing the middleware.
Besides CORS, Video Conferencing systems also secure conversations with DTLS, SRTP, and JWT tokens.
Ⅱ. Media Streaming Protocols
A Video conferencing systems rely on several critical protocols for media transmission and we are bringing to you the most critical ones among them:
1. Real-Time Transport Protocol (RTP)
RTP is popular for one-way transport of real-time audio and video streams.
It is also well-known for tasks like reconstructing time, detecting loss, identifying content and secure conversations.
The best examples of video conferencing platforms using RTP include video-on-demand apps and IP telephony.
2. RTP Control Protocol (RTCP)
The protocol monitors data delivery in video conferencing apps. It works alongside RTP to analyze the quality of the video streams and send feedback on them.
The protocol also monitors how well the media streams sync. RTCP does all of these in a traffic bandwidth as low as 5% when compared to RTP.
3. Real Time Streaming Protocol (RTSP)
This unidirectional streaming protocol is used to deliver live audio and video streams by establishing sessions between client end points. It uses TCP to initiate end-to-end connection from its server.
RTSP is capable of interacting with HTTP. This way a web server and media server can specify different end-points, so the client can select an appropriate combination of media for the conversation.
Ⅲ. How Video Conferencing Works in Apps and Web
Step 1: Connect Users
- The easiest way for 2 users to connect over video conferencing is by visiting the same website. This web page uses a WebSocket API to identify each browser and connect them on a shared signaling server like Node.js
Step 2: Signaling Begins
- Once the browsers (Clients) identify each other, they start sharing critical information about each device like IP addresses and ports. They use a combination of XHR + Google AppEngine Channel API, XHR polling, WebSockets and Server-sent events to establish a WebRTC communication between each other.
Step 3: Generate and Find ICE Candidates
- Once the signaling is completed, the browsers start to discover the connection paths using the ICE protocol.
- In the “finding candidates” process, the ICE protocol uses the STUN/ TURN server to establish connection between their browsers and traverse their NAT devices by mapping them with a directly accessible network interface and port.
Step 4: Negotiate Media Sessions
- At this point, both the browsers can identify and communicate with each other. Subsequently, they start agreeing upon the type and format of the audio and video streams, and start exchanging resolution, codec and bitrate.
- This negotiation of data takes place based on the offer/ answer model using the Session Description Protocol (SDP).
Step 5: Begin RTC Streams
- Finally, the browsers can start streaming their audio and video media to each other, either directly via a P2P connection or via any media relay gateway.
Step 6: Establish Communication & Deliver Media
- As further development, the multiple devices start connecting to a Content Distribution System.
- These devices can leverage the multi-bitrate encoding to adjust to multiple different resolutions automatically in accordance with their internet quality or device performance.
- In addition to this, the platforms can also use Quality of Service (QoS) solutions to optimize the video, audio and screen sharing experiences.
8 Types Of Video Conferencing For Teams
1. Point-to-Point Video Conferencing
This is nothing but connecting 2 individuals over a video call. As the name indicates, it connects 1 point to another point
i.e. one location (user 1) to another location (user 2) to enable direct two-way communication.
2. Multi-point Video Conferencing
Simply put, these are group video calling/ conferencing. These calls connect three or more locations at the same time over a single call or network.
This enables multiple participants to meet virtually to talk to each other, share content and collaborate for tasks or discussions.
3. Telepresence Video Conferencing

This is a 3-D video conferencing technology. It goes beyond regular video calling with elements like lighting, room design, and robotics to simulate face-to-face interactions as if the person is right in-front of you, in the same room.
4. Desktop Video Conferencing
This is simply the use of a desktop to connect over a conference call rather than using a dedicated hardware in a conference room.
This means, users can connect through video conferencing apps or browsers on their personal laptops or computers, using built-in or external webcams and microphones.
5. Mobile Video Conferencing
This is the easiest way to connect over a video conference – to use the app in a mobile device that can connect multiple people via video and audio over an IP network.
6. Web-based Video Conferencing
This is the form of online meeting where users can simply get onto their mobile or web browsers and start joining a conference.
All they need is an internet connection to meet or talk to each other virtually.
7. Integrated Video Conferencing Systems
As the name indicates, an Integrated Video Conferencing System is a combination of both hardware and software that brings together camera, mics, speaker and CPU along with software to share screen, use white-boards or enable mute/ unmute controls, with access across any preferred channel like desktop or mobile.
8. Service-Based Video Conferencing (Cloud Video Conferencing)
This type of conferencing technology uses remote servers + internet to enable video meetings. Users need not rely on local hardware or servers to connect to these meetings, rather a simple web-connected device is sufficient.
13 Core Benefits Of Video Conferencing In Business Apps
Although Video Conferencing cannot fully replace face-to-face interactions, it still plays a critical role in business communication for the following reasons.
- Flexibility and accessibility: Video Conferencing makes face-to-face communication easier than ever. Users need not book costly plane tickets to commute to locations where meetings happen. Even if they live on the other side of the globe, they can connect online instantly and make their presence worth it.
- Saves Time: The setup is quite simple. You just open the app, click on the video call, add participants and make large-scale meetings happen within minutes. Neither you nor your team will need to spend your time making arrangements for a meetup to happen.
- Cost Savings: Video Conferencing saves your money. You get to keep the money that you might have to invest on locations, and accommodations to bring people together for a discussion, if offline.
- Accommodate Learning From Anywhere: Video Conferencing has made learning easier and accessible. Especially, after the pandemic era, Virtual Video Conferencing has made it possible to tutor students and reach education right to their homes, through screens.
- Enhanced Visual Interaction: Audio calling is good, but video calling makes interactions and collaborations more lively and effective.
- Easier Multi-participant Conversations: Not just 2 people, Video conferencing can connect two to hundreds of users on the same call, or switch to streaming, to host millions of users on a live session.
- Conversational Fluency: Video calling helps people converse with each other quickly and actively, making visual engagement drive fluency in the discussions.
- Interpersonal Awareness: Unlike audio calling, video conferences help people stay active during a discussion, since everyone on the call can see facial expressions of agreement, disagreement or boredom.
- Attentional Focus: Video Conferencing helps students or employees focus on the calls with interactive elements like white-boarding or screensharing, keeping sessions more lively and active.
- Effective Co-ordination: Since video conferencing connects everyone on the call face-to-face, coordinating with each other gets easier and clean.
- Corporate Productivity: Business organizations from startups to large-scale enterprises make use of Video Conferencing to meet virtually for tasks/ projects, and get things done effectively.
- Multi-disciplinary Discussions: Not just one department, any or every part of the organization, whether tech teams, doctors, technicians, marketers or management, people can connect over conferences and work for a common cause or goal.
- Scalable Communication: A conference room may accommodate hundreds to thousands of users and might have a limitation. But video conferences do not have any. You can host millions of people, having them wherever they are. On the other hand, Video Conferencing also can connect just 2-3 people, if needed. They can scale up or down just as you need it.
12 Key Features of Video Conferencing Software

The picture speaks for itself. HD video and audio are fundamental requirements of a video conference.
With advancements in technology, modern Video Conferencing platforms are able to deliver calls at 4K Ultra HD resolution, along with AI-powered background noise cancellation capabilities for clear visuals.
1. Screen Sharing
Screen sharing enables participants to present their content to other participants, and collaborate on documents in real-time. They also include annotation capabilities, and seamless switching between different sources.
Modern apps also come with options to share specific apps or windows rather than entire screens.
2. Chat & Messaging
One of the easiest ways to drive interaction on video conferencing platforms is by adding text-based interactions.
Participants can send messages during an ongoing conference, share links, or feedback in public or privately to the host.
3. Breakout Rooms
This feature in a video conference lets the host divide a large meeting into smaller, focused discussion groups. They can assign participants to specific breakout rooms either automatically or manually, and allow seamless transition between main sessions and breakout rooms.
The host can also record the sessions independently, and manage each breakout activity with unique admin controls.
4. Meeting Security
Video meetings, especially large scale conferences have huge security risks like intrusion of unauthorized participants and theft of user information.
To control and manage them, it is recommended to include end-to-end encryption, filter out malicious participants in waiting rooms and implement robust authentication systems.
5. Mobile & Cross-Device Support
Video conferences must be capable of operating on any device. Especially in an era where people work on remote settings and during travel, the functionality must work on any device a user prefers.
6. Integration Capabilities
Having a video conference app as a standalone platform excluded from your business system may cause more work friction and disturb the user experience.
Go for solutions that are capable of operating hand-in-hand with your CRMs, project management tools and calendar systems.
7. Recording and Transcription
Recording and transcription features are both critical elements in capturing important discussions in a video conference.
Organizations can record HD video and audio of their meetings and store them securely for repurposing or reference purposes.
On the other hand, transcription facilities provide options to search texts, identify users and automate summaries.
8. Background Noise Removal
This is a critical feature especially in a professional setting like podcasting, remote team meetings and client calls.
Video conferencing systems need a functionalities that can automatically detect unwanted background noise in recordings, streams and video communications.
Modern systems these days come with AI-powered capabilities that use convolutional neural networks (CNNs) and recurrent neural networks (RNNs) to perform automatic noise detection, batch processing, one-click audio cleaning, speech enhancement, and filler work removal.
9. Virtual Backgrounds
Virtual background is a technology that enables participants to blur their physical backgrounds, or replace them with custom photos to maintain a professional appearance during calls and protect their privacy.
10. Closed Captioning and Real-Time Translations
CC is an essential feature that adds real-time transcriptions that improve comprehension in multilingual environments, and in conferences that include participants with hearing impairment.
Several businesses these days adopt AI-powered Speech-to-text solutions to convert spoken words in a meeting to text transcriptions.
11. Polls, Q&A, & Reactions
Video conferencing apps include engagement and feedback collection features like polls and Q&A to enable participants to actively interact in a conference, and to facilitate the host for better decision making.
12. AI Assistants
Automation is the trend everywhere and video conferencing is no exception.
Video conferencing platforms include AI assistants that can automatically create meetings, schedule them, prepare reports, provide real-time transcripts, summarize meetings and generate follow-up tasks.
Which Industries Use Video Conferencing?
1️⃣. Business Communication
Organizations small and large use video conferencing as a critical tool for team collaboration, client meeting and remote work setups.
They reduce huge expenses on travel to work premises and improves the operational efficiency of teams.
2️⃣. Education & E-Learning
Research indicates that there is an increase in use of video conferencing for face-to-face lectures, post COVID-19 pandemic.
These tools help maintain educational continuity without disruptions and to reach students through courses and sessions remotely.
3️⃣. Healthcare & Telemedicine

Doctors can provide virtual consultations to patients and offer remote diagnostics.
On management aspects, healthcare professionals can perform interdisciplinary team meetings and for continuous medical education.
4️⃣. Customer Support & Sales
Video conferencing connects service representatives and customers via face-to-face interactions.
They enable sales teams to deliver product demos, and for personalized consultations to clients and customers.
5️⃣. Recruitment & HR
Human resource departments utilize video conferencing for remote recruitment and employee onboarding activities.
Besides, the technology also supports functions including employee training, performance review meetings and candidate screening.
6️⃣. Legal & Government Services
Legal organizations use video conferencing for court proceedings, client consultations, administrative meetings and client consultations.
On the other hand, government sectors can use these tools to coordinate public meetings and emergency discussions.
7️⃣. Events & Webinars
Event management teams can easily gather a large group of people for conferences, concerts and community events online, when hosting global audiences or prefer a virtual session, so users can participate from anywhere.
Similarly, organizations can use a Video Conferencing system to conduct training sessions, and conferences to cater a huge scale of audience.
8️⃣. Media & Content Creation
Video conferences are an ideal tool for media teams, as each department may work from different regions. The recording team might not be in the same place as the editing team is, nor the creative strategy team.
In these circumstances, video conferencing apps bring them all in one place for content review or client feedback.
Ready-made vs Custom-built Video Conferencing Apps
Off the shelf (OTS) video conferencing tools like Google Meet and Microsoft Teams are great. You can go to their official website, purchase the app and start video conferencing with your teams.
But do they work just as you need it?
Or If you are a business and want to connect with your customers, are these tools perfect for delivering on-brand experience?
Almost all the time you need to gather your customers, clients, partners or team, you might have to step out of your platform, open these third-party software and start conversations with limitations on brand-specific features.
The good news is – You can Build your own Video Conferencing Platform in under 48 hrs.
Before we get on to understanding how to build your own Video Conferencing app, let’s analyze both the options.
Third-party apps vs Custom-built apps
Ⅰ. Third-party ready-made apps
If you are a small to medium-sized business, starting off with a pre-built video conferencing app is a great idea. They are easy to purchase, set up and use.
You’ll only need to spend a few bucks for adding these platforms to your business strategy.
Ⅱ. Custom-built video conferencing apps
As the name indicates, you can build these apps with almost complete customization.
You can add features, user experience and integrations just as you need it, and create workflows that align perfectly with your business requirements.
You’ll also have complete ownership of the codebase, giving you full control over the data, infrastructure, and security.
How to build custom-built video apps? There are 2 options and let’s look into them elaborately in the upcoming section.
SDK-based implementation vs Building from scratch
Ⅰ. SDK-Based Implementation Considerations
Video Conferencing SDK (Pre-built) come with production-ready features for building modern video conferencing apps.
They are designed with only a few lines of code, making it simple, quick and easy to implement into any app.
These solutions are also built to handle WebRTC complexity which is one of the biggest challenges when building from scratch.
Developers need not worry about the deployment issues and scaling requirements. The vendors take care of these critical criteria along with support for network optimization and maintenance.
Ⅱ. In-House Development (Build from Scratch) Considerations
If you are planning to build your video conferencing app all by yourself from scratch, here’s a quick warning: the development timeline might be longer than SDK-implementation.
You’ll also need to take care of the capabilities of your technical team and the infrastructure requirements. Your team might also have to take up the ongoing maintenance responsibilities.
Most businesses choose these in-house development options as they focus to have complete control over the entire codebase. The other case is – a few businesses aim to build extremely specific use cases.
Cost-Benefit Analysis
Ⅰ. Financial Considerations
You can purchase an SDK for a one-time license cost or for a monthly subscription, depending on your requirements. This will include the APIs, SDKs, libraries, deployment and maintenance.
When you build from scratch, you might have to pay for the technologies, your team, upgrades and updates for your software, subscription charges for additional services and hardware or server equipment, which is a huge sum when compared to going for a SDK subscription/ license.
Ⅱ. Time-to-Market Factors
Building your video conferencing platform with a pre-built SDK gets done faster within some 10 mins to 48 hrs, when you choose the right video conferencing solution provider.
Contrastingly, building from scratch will take somewhere around 9 months to 1 year minimum to deploy and launch an MVP with at least the basic features.
Common Video Conferencing Challenges & Recommendations for Choosing SDKs
In this section, we’ve taken a case study in selection of video conferencing services by the Flinders University Telehealth in the Home trial (FTH Trial) published by Alan Taylor, G.Morris, C.Carati and 3 other authors.
We’ll compare the most common challenges the users faced in video conferencing platforms and the recommendations provided by the experts.
Challenge 1: The UI was not easy
The elderly patients in the case study found the UI of the video apps complex. It was not easy for them to configure the app, enter credentials or navigate across. Sometimes, the errors in these apps confuse the users.
Recommendation: Choose a vendor who lets you customize the user interface with clear labels, navigation menus and clear audio/ video cues, perfectly curated for your end users.
Challenge 2: The platforms were not compatible for the apps
Many consumers found that they were not able to access video conferences on their device as the apps were not compatible with their device OS.
Recommendation: Check if the solution you choose can work on any device, and any platform, so users can access your app on any device they prefer.
Challenge 3: Interoperability issues
Different providers used different systems (e.g., SA Health used Cisco Jabber) causing risks of data leaks across groups and services. Subsequently, network security policies prevented inbound calls.
Recommendation: Go for multi-tenant on-premise setup to isolate one group of users when allowing another according to their access levels.
Challenge 4: Performance issues
Some users had to reboot their devices as the video conferencing app on their app stopped working or froze the device due to network fluctuations.
Recommendation: Select a vendor with solutions that lets apps work on any network condition. Adaptive frame bitrate is a wonderful technology that the SDK must have to prevent these delivery challenges.
Challenge 5: Privacy challenges
There were risks of patient data going out of the system if cloud-hosted with weak encryptions.
Recommendation: Pick the solution that has a multi-tenant environment to isolate user accounts. Go for vendors that offer custom security so you can add any layers of encryptions and privacy layers to your platform.
Besides these recommendations based on practical challenges on the user end, here are a few things you may need to keep in mind as a business owner or a developer:
- Customization: Your app needs to stand out in features, functionality and brand identity and customization is a basic requirement for all of these needs.
- Evaluate Core Features: You must not be put in a situation to go for third-party solutions besides your SDK vendor for advanced or additional features. Make sure the vendor you choose has all and above the features you have on your prep list.
- Ease of Use: Investing on an SDK is a great option. But that must not lead your teams to rely on extensive support to implement the SDK. It must be easy to integrate like plug and play solutions so you need not make any extra efforts to launch it on your system.
- Codebase Access: Most businesses take the risk of building their own video apps from scratch only because they fear losing their codebase access to third-party vendors.
- But there are other secure options – Go for vendors that give you all the control over your source code, user data and infrastructure without any limitations. This way your data stays under your ownership and no external parties can have access to it.
How Can MirrorFly Help?
MirrorFly has been in the industry for almost 17+ years and supporting businesses that build video conferencing into apps has become pretty-much a part of our daily lives.
This is a team who’s got it all ready for you – from pre-built video conferencing solutions to high-end servers, an “yes” to our product and service have resulted in 100+ video conferencing apps you can find in app stores right now.
So, how can we help you with video conferencing?
Custom Video APIs & SDKs
We’ve talked about it in the sections above. How advantageous it is to use custom video conferencing APIs and SDKs for apps.
We provide them – tested and tried by Fortune 500 brands, these solutions have been acclaimed for their 100% customization allowing businesses to build Video Conferencing apps just as they want to.
Full Data Control, No Hidden Access
‘Building from scratch gives access to the entire codebase’.
We’ve turned this into a myth by offering our solutions with full control of the source code, which consequently leads to full control over your user data, infrastructure and security.
This means you can white-label your video conferencing app with your own brand elements and UI components.
Deployment – Anywhere You Point At
There’s no limitation on where you’ll launch your app. You can choose MirrorFly’s multi-tenant chat server or self-host it on your on-prem servers or cloud, just as you want it.
MirrorFly prioritizes your requirements and there’s no restriction on where you deploy your video conferencing system.
Features – Advanced & Beyond
When you sign up MirrorFly as your CPaaS provider, you get access to 1000+ custom video conferencing features.
When we mean custom, we mean – you can customize any part of the feature and personalize it to your needs.
Flexible Pricing
Considering different budgetary requirements, MirrorFly comes in 2 different pricing models – Software as a Product (SaaP) that provides solutions at a one-time license cost for lifetime access to features.
The other option is Software as a Service (SaaS) that starts from $0.08 per month.
Integration Support + Dedicated Team
Need a hand for integrating the solution into your existing app? You can connect with MirrorFly experts who can help you with end-to-end implementation.
Or you can hire a dedicated team of experts who can build the entire app for you.
Interested? Leave us a quick note about your requirements.
One of our experts will get in touch with you in the next 24 hrs!
Cut months of dev work. MirrorFly SDKs give you WebRTC, security, and APIs to launch video apps in hours.
Contact SalesWebRTC pre-built stack
HIPAA-compliant security
Scale without limits
