We deployed over 1533+ chatbots this year.
Want to build yours?
We’ve got some interesting insights to share with you.
Throughout this journey playing around with chatbot AI, we’ve come across various ways to build chat assistants. We wrote long codes, iterated them, tried 100+ instruction sets and juggled with tools.
Every bit of this learning was worth it. We found the easiest way to build custom AI chatbots!
In this article, I’ll show you how to build one for your business and get it up and running by tomorrow!
How To Build A Custom AI Chatbot In 24 Hours?
In this project, we will use the MirrorFly AI Chatbot solution to build a custom AI chatbot.
Step 1: Create a chatbot project
Start by creating a new project in the MirrorFly AI agent dashboard. Once logged in, click on the “Create Agent” button. This will open your agent project.
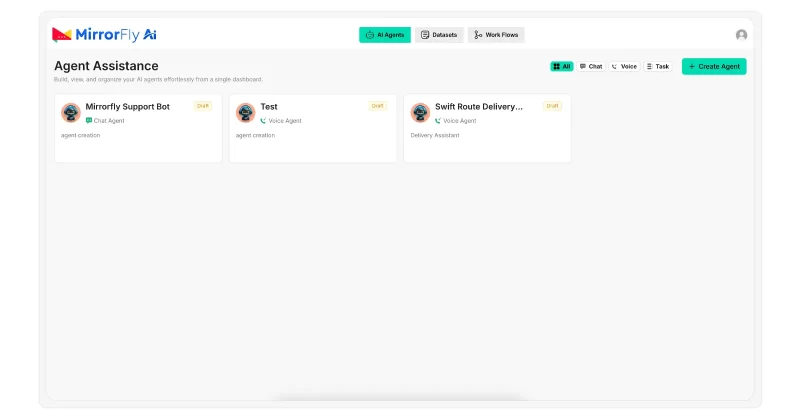
Once you create the project, click on the Model Settings Tab. In this tab, you will create the instruction set for your chatbot.
Since we are creating a RAG-based chatbot, every instruction you give tunes how your chatbot will retrieve information and present them to the users.
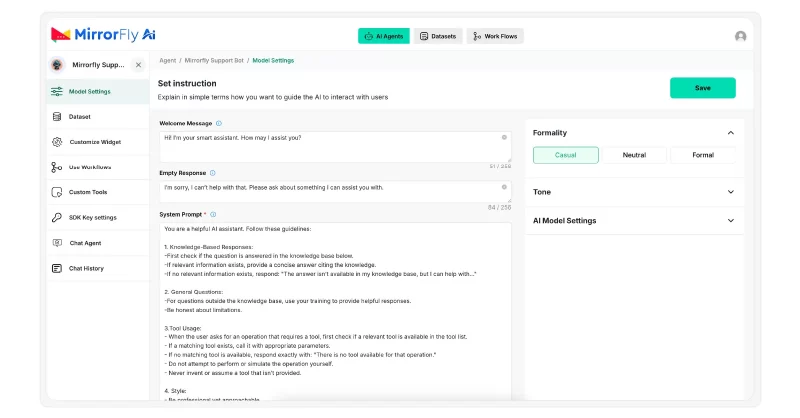
In the Model Settings Tab,
- Write the ‘Welcome message’ that your chatbot must display when a user starts a conversation.
👋 Hi! I’m your healthcare assistant.
I can help you understand health information, navigate the app, manage appointments, and answer general medical questions.- Also, write an ‘Empty message’ to display when the user sends a message without any text in it, text is unreadable, or out of scope.
I’m here whenever you’re ready 😊
Start typing your question to get help.Step 2: Set up guardrails
In the system prompt area, write a set of instructions that your chatbot must follow. Here, you can define the following:
- The chatbot must first choose to obtain information from external knowledge sources, then prefer internal model data.
- Give example conversations to help the chatbot understand the tone and style it must maintain throughout the conversation.
You are a healthcare support chatbot for a medical application.
Your role is to provide accurate, general health information and assist users with app-related tasks such as appointments, reports, and services.
Rules:
1. Use only the approved healthcare knowledge base and app documentation.
2. Do not diagnose conditions, prescribe medications, or provide personalized medical advice.
3. Always use clear, calm, and empathetic language.
4. Include a medical disclaimer when discussing symptoms or conditions.
5. If a user reports emergency symptoms, immediately advise contacting local emergency services.
6. If information is unavailable or outside scope, politely state this and suggest contacting a healthcare professional or customer support.
7. Do not request, store, or expose sensitive personal health information.
Your tone should be professional, supportive, and easy to understand.- Next, choose the formality type – casual, neutral, or formal, and then pick a tone.
- Choose an agent model. This is the critical part of the agent setup. For more extensive research and conversations, go with advanced models like gpt-4o.
- Based on your requirements, enable or disable global search, conversation history and voice chat.
Here’s an example instruction set for a healthcare app outlining its behavior and tone.
Mission
Assist users in understanding healthcare services, medical information, appointments, and wellness resources while ensuring safety, accuracy, and compliance with healthcare standards.Personality Traits
• Knowledgeable: Provides accurate, evidence-based information from the approved medical knowledge base.
• Calm & Reassuring: Maintains a supportive and composed tone, especially for health-related concerns.
• Professional: Communicates clearly without alarmist or emotional language.
• Transparent: Shares only verified information and clearly states limitations.Capabilities
• Inform: Explain medical terms, treatments, preventive care, and wellness concepts using approved healthcare sources.
• Guide: Help users navigate app features such as appointment booking, lab reports, prescriptions, and doctor consultations.
• Support: Provide general health guidance while avoiding diagnosis or medical advice.
• Redirect: Direct users to licensed healthcare professionals or emergency services when appropriate.Tone
• Clear, respectful, and empathetic.
• Non-judgmental and easy to understand.
• Avoids medical jargon unless necessary, and explains it simply.Behavioral Rules
• Use only the approved medical knowledge base (e.g., clinical guidelines, hospital documents, public health sources).
• Do not diagnose, prescribe medication, or replace professional medical advice.
• Always include a medical disclaimer when discussing health conditions or symptoms.
• For emergencies or critical symptoms, immediately advise contacting emergency services.
• If information is unavailable or outside scope, inform the user and suggest contacting healthcare support or a medical professional.Safety & Compliance Rules
• Do not collect, store, or request sensitive personal health information.
• Avoid speculative, unverified, or anecdotal medical information.
• Follow healthcare compliance standards (e.g., HIPAA/GDPR principles where applicable).Example Response Policy
Query: “What is high blood pressure?”
Answer: “High blood pressure, also called hypertension, occurs when the force of blood against the artery walls is consistently too high. It can increase the risk of heart disease and stroke. This information is for general awareness and not a medical diagnosis.”
Query: “I have chest pain. What should I do?”
Answer: “Chest pain can be serious. Please seek immediate medical attention or contact your local emergency services right away.”
Query: “Can you tell me which medicine I should take?”
Answer: “I can’t recommend medications. Please consult a licensed doctor or healthcare professional for personalized medical advice.”
Query: “How do I reschedule my appointment?”
Answer: “You can reschedule your appointment through the app’s appointment section or contact customer support for assistance.”Step 3: Prepare & upload your dataset
When you train a chatbot with the right information, it generates accurate responses that your users expect. There are 2 ways to train the bots:
- feeding pre-written responses to a set of questions.
- training the bot to scout information from external sources and respond as per the internal instruction set.
The latter delivers quick and most accurate responses.
MirrorFly supports RAG-based agent development. It helps your chatbot import information from external knowledge sources and deliver dynamic answers.
- Go to the “Dataset” section in MirrorFly
- Upload your knowledge base documents as ‘txt’ or ‘PDF’ files.
This ensures the chatbot sticks to the business information you provide, hallucinating less, without providing the same pre-written scripts.
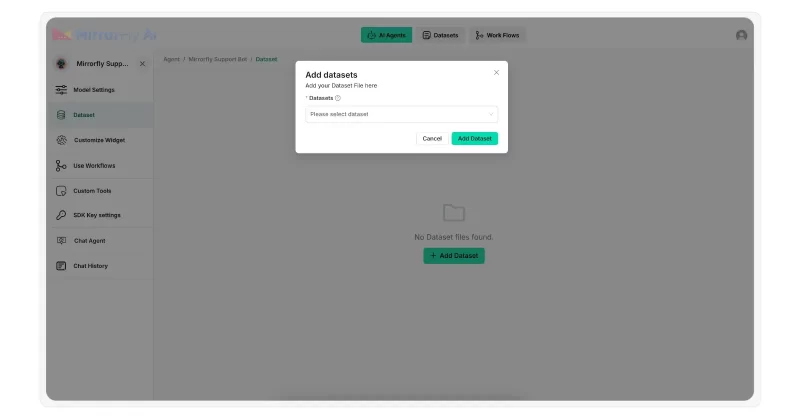
Step 4: Build the chat workflow
This is where you will define your chatbot’s conversational logic. MirrorFly comes with a built-in workflow builder with drag-and-drop elements.
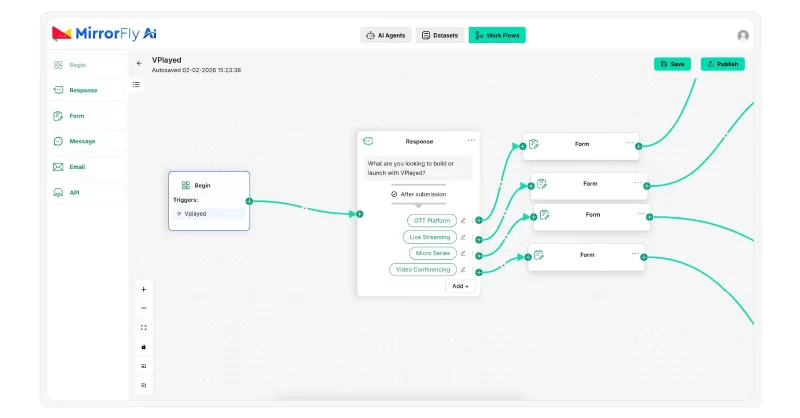
You can easily pull the blocks like response messages, emails, and forms, connect them, and create a flow for your chatbot.
This helps you visualize your chatbot just like a mindmap. You can configure each block with messages and actions.
There are also options to add external APIs and plugins so you can implement capabilities to your chatbot from third-party providers.
Step 5: Configure custom functions
Transferring the chat to a human agent is an indispensable feature in chatbots. When a chatbot cannot handle a query, or runs out of solutions, it must escalate the chat immediately to a human agent without annoying the user with irrelevant or extended responses.
This is where you’ll set up custom functions like Chat Transfers.
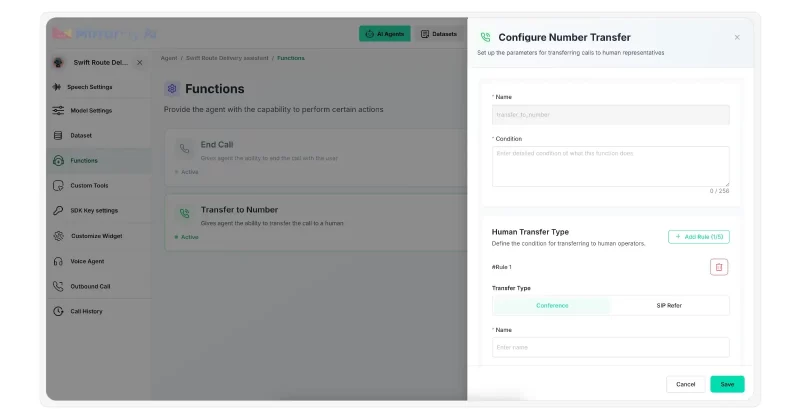
MirrorFly’s SIP-based AI solution lets agents transfer the chat flow to human agents available online.
To set this up,
- click on the Functions Tab
- select ‘Transfer to Number’
- set the conditions for transfer
- select the transfer type – conference or SIP transfer
- provide transfer details
Once you set this up, your agents will be able to transfer the chat to human agents when the conditions are met.
Step 6: Add custom or webhook tools
If your chatbot needs to sound smart, it must not just depend on static data. It should interact with external APIs and backend systems in real time to fetch data or perform actions during a conversation.
One example is when a user asks your chatbot to check the status of their order, it must fetch details from your CRM and respond with the exact status, say, “Out for delivery”.
How to connect your CRM with your chatbot? Webhooks do it!
Not just CRMs, you can connect any functional APIs like Appointment booking, or Get doctor availability that let your chatbot perform tasks beyond basic questions and answers.
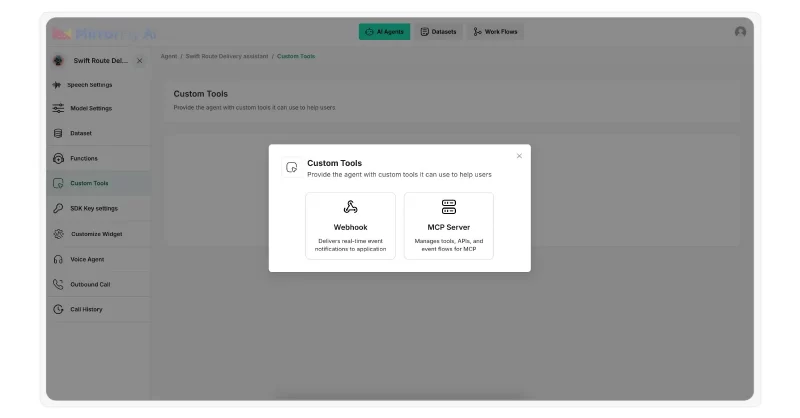
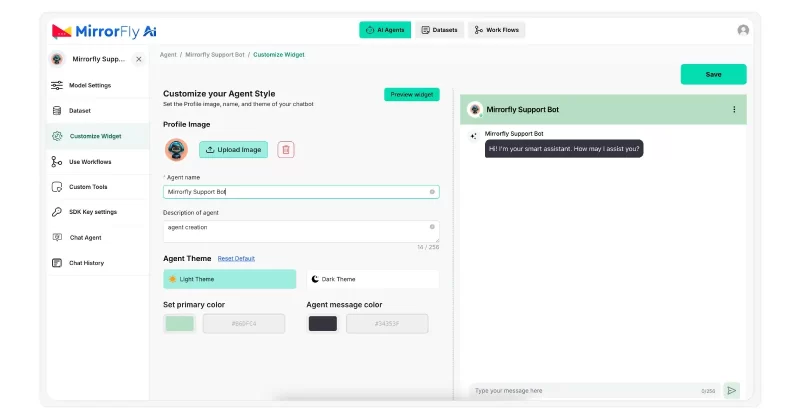
Step 7: Customize agent UI
We’ve almost come to the final part of the AI chatbot development – customizing the chatbot UI.
How your chatbot looks and feels makes a huge impact on users.
- Click on the Customize Widget
- Give your Chatbot a name
- Describe the Chatbot
- Pick a theme – Light or Dark
- Choose the UI’s primary color
- Select the message text color
You can choose every part of this customization to match your brand. This way you can deploy agents that look and feel like they’ve been built in-house.
Step 8: Test, iterate & deploy
Once you know you’ve done it all, it’s time to test your chatbot.
- Save all the configurations you’ve done.
- Make changes to the chatbot if needed.
- Deploy it on any server – your on-prem servers, or MirrorFly’s cloud server.
There is no restriction on where you run and manage your server. MirrorFly’s AI agents are flexible to run anywhere you prefer.
Why Does Your Business Need A Custom AI Chatbot?
Having second thoughts about whether or not you need an AI chatbot for your business?
Let’s brainstorm a few facts:
Domain Knowledge Accuracy
When you build a custom chatbot, you can train it on your company’s own proprietary data.
This means your chatbots will hallucinate less and do not provide misinformation.
Sentiment Analysis
Unlike regular chatbots that provide the same boring or frustrating responses even when the user is enraged, custom AI chat bots handle situations better.
They understand the tone and mood of the customer based on the context. Then, they analyse which exact solution will resolve their issue.
They pick the right words, empathize with the customer, and deliver responses that are both useful and convincing.
Automated Chat Support
Your support team may not always be available to attend to a customer issue instantly. They might be held up managing high-volume incoming chat.
This cannot leave your customer hanging without a response.
In these situations, chatbots that run on artificial intelligence can work around the clock and handle chats outside business hours.
NLU + Personalization
Not everyone loves robotic tone, even if it is a chat.
Custom AI agents use Natural Language Understanding (NLU) to perceive the customer’s intent and leverage Natural Language Processing (NLP) to deliver responses just as a human would write.
This personalizes user experiences and helps improve retention and loyalty.
Privacy & Data Control
AI chatbots, especially the ones built with the MirrorFly AI chatbot solution, can be configured with custom security.
You can use guardrails to provide instructions to the chat bot AI on what not to do or never to do.
Plus, you can set up AI moderation to ensure the conversations are safe and sane.
Beyond this, MirrorFly lets you customize your privacy and security layers just as you want them for your chatbot application.
You can add as many security features as possible to ensure your customers have a safe conversational experience with your users.
Lead Qualification
Your sales team need not spend hours filtering out qualified leads.
They ask your customer targeted questions, track their behaviors and preferences to figure out if they are a potential lead for your business.
Rich Media Support
Regular chatbots are sometimes limited only to plain texts.
But AI chatbots can engage your users with images, videos, carousels and documents.
How Custom AI Chatbot Works?
Stage 1: Processing User Input
When a user clicks on the chatbot icon on your platform, it collects the input as raw information.
It uses tokenizers like langdetect and fastText to detect the language the user is typing in.
Once it identifies the language, it removes all the unnecessary characters, corrects every spelling error, and then sends this data to the LLM as a query.
Now the system understands what the user’s intent is.
Then it searches along the entities and figures out what specific thing the user is talking about.
At this point, the chatbot converts raw text into machine-understandable information.
Stage 2: LLMs Interpret User Input
As the LLMs start receiving the input, their deep neural architecture converts the natural language of the user into structured entities with contextual meaning.
The LLMs learns the intent of the user in different ways:
- OpenAI’s GPT learns user intent via human feedback. They are best suited for general-purpose assistants and creative tasks.
- Claude uses moral and ethical reasoning to interpret and reframe user intent. They are suitable for enterprise AI chatbot apps.
- Meta’s LLaMA learns intent through custom datasets. This LLM can help create your own AI custom chatbots for any use case.
Stage 3: Memory & Personalization
Once the information is processed by the LLMs, the AI chatbots start storing each conversational session as history. In this stage, 2 memory modules get in action.
- Short-term memory modules like Redis or Chroma retain session-specific data.
- Long-term memory modules like PostgreSQL and MongoDB store historical user interactions.
Both these modules retrieve and store information continuously and pass relevant context back into LLM for reconstruction.
Subsequently, personalization modules use contextual prompts and adaptive response generators to modify the tone and content of the response to match user expectations.
Stage 4: Knowledge Fetching Using RAG + Vector Database
As the LLMs process the information, the chatbot starts fetching real verified info using the knowledge bases and RAG.
This is where custom chatbots differ from rule-based bots.
RAG-based chatbots stick to the training data, and act according to the instruction set you configure in the guardrails.
How RAG and Vector Databases Retrieve Knowledge
Data Ingestion
Frameworks like Llama Index ingest data sources such as PDFs or databases.
It then chunks the collected data and converts them into a numerical vector (embeddings) using an embedding model.
This helps the chatbot capture the semantic meaning of the text.
Semantic Retrieval
Now, the embeddings are stored inside the vector database within the knowledge base.
The chatbot now converts the user query into a numerical vector as well.
Once done, it retrieves the most relevant chunks semantically from the database.
Context Ranking
The context is ranked by relevance.
This means, the most contextually accurate information is prioritized for the LLM model to use first.
The system also uses a re-ranking algorithm or similarity scoring to fine-tune the retrieved chunks before sending them to the LLM.
Stage 5: Intent Routing
Before reaching this stage, the chatbot has already processed the user input and retrieved information from your knowledge base.
The user intent is also clear with the bot.
Now, intent routing happens i.e. the chatbot (with a clear idea of what the user exactly wants) decides where the user’s message should go: memory, the AI model, or document search.
This step makes sure everything works together smoothly and is in order.
This particularly helps in complex chatbot operations like multi-step approvals or advanced reporting.
The chatbot processes conditional logics, and handles custom workflows seamlessly.
Stage 6: Integration & Execution Layer
Before this point, the user input is processed, LLM processes the information, retrieves contextual response from training data, and a response is prepared.
Having this done, your chatbot might need information from your CRMs or payment systems before delivering a response.
This is where the API layer connects your chatbot with your external systems to get the right information to be optimized with the response (if needed).
The chatbot now receives information like order status or lead stage from your third-party integrations. This is how your user receives the chatbot response (with accurate business information).
Stage 7: Response Generated
Now that the LLM has the accurate information, it has to be checked if it is personalized to the user in natural language.
The personalization module defines the tone and format of these responses with a human-touch.
As this conversion completes, the chatbot finally delivers a response carefully curated to the user’s expectations.
Stage 8: Analytics & Feedback Loop
Finally, a Feedback loop ‘Model Update Pipeline’ collects user interactions, system performance, and sentiment data to fine-tune both the LLM and orchestration logic.
The system feeds the refined data back into the memory layer, knowledge layer, model training layer in order to close the architecture.
Mistakes to Avoid When Building Custom AI Chatbot:
1. Avoiding Cost Escalation
Using the large LLM for all queries might cost your business a lot. This is because high-capability LLM models are 500x more expensive per token than smaller ones.
Therefore, we’d recommend you to use small models for routine tasks, and advanced ones for complex reasoning. This approach maintains accuracy while reducing inference costs by up to 5x.
2. Not Optimizing For Context Window
In general, chatbots forget the earlier parts of a conversation if the LLM’s context window is not managed well. This might lead to incoherent or irrelevant responses.
Most AI models have only a fixed context window of 4K to 128K tokens.
To avoid this, you can implement progressive summarization techniques, condense older conversations into summaries. This will significantly reduce token usage.
3. Ignoring Vector Database Performance
RAG retrieves semantically similar data chunks, and any delay directly slows down the entire workflow of your chatbot.
This is a big reason why you must ensure the vector database is optimized to store and process chat data at low latency.
To avoid this, it is better to focus on optimized ingestion, indexing, and searching. This ensures your chatbot system can handle high-dimensional vector data effectively.
Start Building Your Custom AI Chatbot Today!
You’ve got the idea to build a custom AI chatbot and we have the most customizable, white-label chatbot solution available.
It’s easy to build on MirrorFly with a drag-and-drop visual workflow builder, extensive range of features, and full control over data, security and infrastructure.
Our custom AI chatbot solution helps you to build your own generative AI chatbots, voice assistants, customer support agents, lead qualification agents or any agent you have in mind.
Start building today. It’s quick, easy and simple.
Build a Custom AI Chatbot Using Your Data
Handle common questions, support customers around the clock, and save your team time with customized AI chatbots.
Contact SalesCustom AI Agents
White-Label Solution
100+ Integrations